Collection
Collection能非常高效的操纵数据。
Collection是一个接口,interface。具体的实现有List、Set等。
List和Set继承Collection接口。Map不继承Collection。
Collection体系:
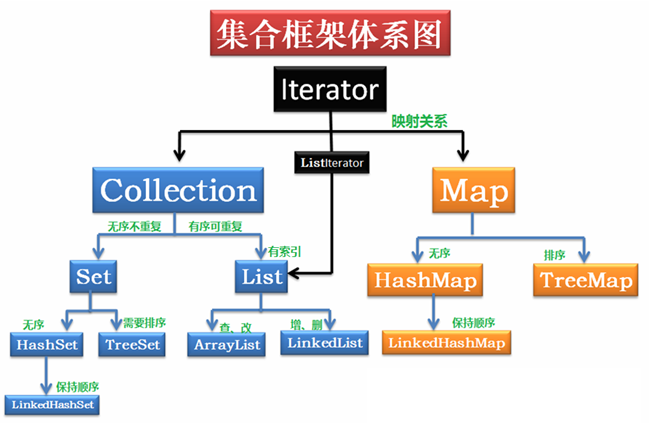
Collection方法有:add(),addAll(),clear(),contains(),containsAll(),equals(),hashCode(),isEmpty()等等。
Collection collection = new Collection();
这样写会报错,collec是抽象的,不能被实例化,collection是一个接口,不是类。
如果xxx可以被实例化,那么xxx里所有的方法都必须要有方法体。
List
List是有序的集合,继承Collection,还提供了一些额外的方法,比如get。
List的方法有:size(),contains(),isEmpty(),stream(),add(),addAll(),retainAll(),clear(),remove(),removeAll()
List有ArrayList,LinkedList。
List常用的写法:
1
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
2
Collection c = new LinkedHashSet();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(c);
2的代码等价于:
Collection c = new LinkedHashSet();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
list.addAll(c);
2的代码还等价于:
Collection<Integer> c = new LinkedHashSet();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
for(Integer i : c){
list.add(i);
}
3关于retainAll
Collection<Integer> c = new LinkedHashSet();
c.add(1);
c.add(2);
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.retainAll(c); // 只保留c中有的
面试题:ArrayList的动态扩容?
每当你想写注释的时候,请先尝试重构,使所有的注释都显得多余
Set
List是有序的,Set是无序的,而且Set是一个不允许有重复元素的集合。
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
现在list里有重复元素
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(list);
这样就没有重复元素了
Java世界里第一重要的约定:equals
Java世界里第二重要的约定:hashCode
hashCode的约定
- 同一个对象必须始终返回相同的hashCode
- 两个对象的equals返回true,必须返回相同的hashCode
- 两个对象不等,也可能返回相同的hashCode
哈希就是一个单向的映射,为什么是单向的?
在Object.java中有public native int hashCode();,hashCode的返回是int,int的数量限制为正负21亿,最多有42亿种可能,而对象肯定是多于这些的,可以创建无限多个对象。因此只能从对象映射到int,不能从int映射到对象。
HahSet
HashSet是最常用、最高效的Set实现。
下面来看看HashSet是有多高效:
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<1000_0000; i++){
set.add(i);
list.add(i);
}
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
set.contains(999_999);
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
list.contains(999_999);
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("set: " + (t1-t0)/1000.0/1000);
System.out.println("list: " + (t2-t1)/1000.0/1000);
运行上面代码之后,我这里显示:
set: 0.0526
list: 8.4076
HashSet是无序的,如果有需要可以用LinkedHashSet。
Map
Map是key-value映射的形式,不能包含重复的key(value可以重复),一个key映射最多一个value。
Map的方法有put,putAll,get(),size(),containsKey(),containsValue(),keySet(),values(),entrySet(),remove(),clear()。
修改map,keySet会变,修改keySet,map也会变。keySet()返回一个Set,values()返回一个Collection。因为Map中key是不能重复的,value可以重复。entrySet()是返回键值对的集合。
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("AAA": "1");
map.put("BBB": "2");
map.get("AAA");
HashMap
HashMap和HashSet几乎完全一样,本质上是一种东西。HashMap的key的set就是一个HashSet。
HashMap会计算key的hashCode,放到对应的哈希桶(存储相同hashCode的东西)里。
HashSet.java里就有HashMap
面试题:HashMap扩容的过程?
面试题:HashMap的线程不安全性?使用ConcurrentHashMap。(Concurrent:并发)
面试题:HashMap在Java7+后的改变:链表->红黑树
TreeSet/TreeMap
Set有HashSet、LinkedHashSet,他们和TreeSet有什么不一样?
HashSet顺序是完全随机的,LinkedHashSet保证和插入的顺序是一样的,TreeSet保证是有序的(TreeSet使用Comparable约定,认为排序相等的元素相等)。
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(100000,196,-2,-45623,5543,15);
Set set1 = new HashSet(list);
Set set2 = new LinkedHashSet(list);
Set set3 = new TreeSet(list);
set1.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("----------------");
set2.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("----------------");
set3.forEach(System.out::println);
可以打印出来上面的代码看看顺序是怎样的。
TreeSet最大的用处是用来排序。
TreeSet内部是红黑树(一种二叉树)
TreeMap是一个有序的Map,他的key就是一个TreeSet。
查找ArrayList需要挨个查找,需要查n次,复杂度为O(n)(线性复杂度),比较没有效率。
TreeSet所用的红黑树,查找一个元素的复杂度为O(log n)(对数)。TreeSet可以提高查找的效率。
Collections工具方法集合
List的工具方法就是Lists,Set的工具方法就是Sets,Collection的工具方法就是Collections。
常用的有
- emptySet(),返回一个空的Map
- synchronizedCollection,将一个集合变成线程安全的
- unmodifiableCollection,将一个集合变成不可变的(也可以使用Guava的Immutable)
Collection的一些不太常见的实现
- Queue/Deque 队列(先进先出)/双端队列(double ended queue )
Vector/Stack被抛弃的类,不要使用。用ArrayList/Deque替代。- LinkedList 链表
- ConcurrentHashMap 线程安全的HashMap
- priorityQueue 优先级队列,堆heap实现的,比Queue更进一步,有优先级。
Guava
番石榴
Google写的,是用于补充Java原生JDK里的一些不完整的Collection实现。
遇到了Collection不能满足的要求,可以试试Guava。
不要重复发明轮子!尽量使用经过实战检验的类库!
https://github.com/google/guava
- Lists/Sets/Maps 工具方法
- ImmutableMap/ImmutableSet 不可变的集合
- Multiset/Multimap
- BiMap 双向的,可以从key映射到value,也可以从value映射回key
HashMultiset set = new HashMultiset.create();
set.add(1);
set.add(2);
set.add(2);
set.add(2);
HashMultimap map = new HashMultimap.create();
map.put(1,1);
map.put(1,2);
map.put(1,3);
map.put(1,4);
打印上面的代码看看。